Common examples of industries recognized for their high and low degree of operating leverage (DOL) are described in the chart below. The DOL would be 2.0x, which implies that if revenue were to increase by 5.0%, operating income is anticipated to increase by 10.0%. Operating Leverage is controlled by purchasing or outsourcing some of the company’s processes or services instead of keeping it integral to the company.
How to Interpret DOL?
A business that generates sales with a high gross margin and low variable costs has high operating leverage. It measures a company’s sensitivity to sales changes of operating income. A higher degree of operating leverage equals greater risk to a company’s earnings.
How Does Operating Leverage Impact Break-Even Analysis?
The catch behind having a higher DOL is that for the company to receive positive benefits, its revenue must be recurring and non-cyclical. One notable commonality among high DOL industries is that to get the business started, a large upfront payment (or initial investment) is required. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
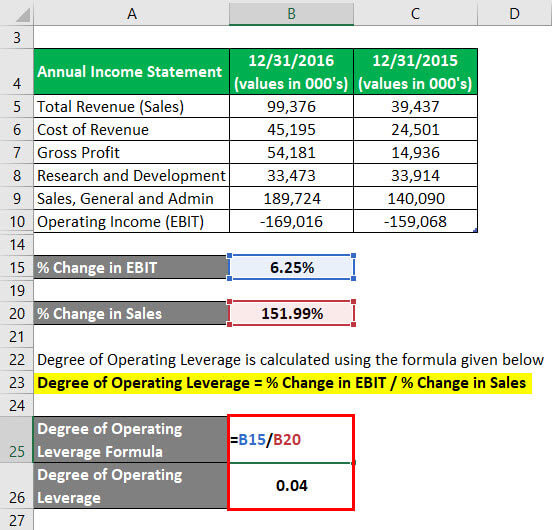
Operating Leverage Analysis Example
The percentage change in profits as a result of changes in the sales volume is higher than the percentage change in sales. This means that a change of 2% is sales can generate a change greater of 2% in operating profits. If a firm generates a high gross margin, it also generates a high DOL ratio and can make more money from incremental revenues.
- Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers.
- This indicates the expected response in profits if sales volumes change.
- We’ll go over exactly what it is, the formula used to calculate it, and how it compares to the combined leverage.
- Running a business incurs a lot of costs, and not all these costs are variable.
- If you try different combinations of EBIT values and sales on our smart degree of operating leverage calculator, you will find out that several messages are displayed.
This allows investors to estimate profitability under a range of scenarios. Companies with a low DOL have a higher proportion of variable costs that depend on the number of unit sales for the specific period while having fewer fixed costs each month. In contrast, companies with low operating leverage have cost structures comprised of comparatively more variable costs that are directly tied to production volume. Running a business incurs a lot of costs, and not all these costs are variable.
Operating leverage is a measure of how revenue growth translates into growth in operating income. It is a measure of leverage, and of how risky, or volatile, a company’s operating income is. Undoubtedly, the company benefits in the short deleting invoices and bills in xero part 2 run from high operating leverages in most cases. But at the same time, such firms are exposed to fluctuations in economic conditions and business cycles. By now, we have understood the concept of Dol, its calculation, and examples.
The degree of financial leverage is a more mainstream ratio used by businesses for accessing the sensitivity of earnings per share by the change in the EBIT. Investors can access a company’s risk profile by analyzing the degree of operating leverage. There are many different methods to do the financial analysis of a company.

This section will use the financial data from a real company and put it into our degree of operating leverage calculator. Although you need to be careful when looking at operating leverage, it can tell you a lot about a company and its future profitability, and the level of risk it offers to investors. While operating leverage doesn’t tell the whole story, it certainly can help.
A second approach to calculating DOL involves dividing the % contribution margin by the % operating margin. This variation of one time or six-time (the above example) is known as degree of operating leverage (DOL). Undoubtedly, the degree of financial leverage can guide investors in investment decisions. Another accounting term closely relates to the degree of operating leverage. But the other perspective of this situation is a lot of costs are tied up in fixed assets like real estate, machinery, plants, etc.
